
If a company follows an accrual basis of accounting, the interest revenue will be recorded in the income statement even if the interest income has not been received. However, if the company had been using the cash basis of accounting and the cash had not yet been received by the end of the reporting period, no interest revenue would be recorded in that period. The main issue with interest revenue is where to record it on the income statement. If an entity is in the business of earning interest revenue, such as a lender, then it should record interest revenue in the revenue section at the top of the income statement. Placing it here keeps readers of an entity’s financial statements from getting the impression that revenue from continuing operations is higher than is actually the case. As such, the latter approach is the more conservative treatment of interest revenue.
Interest Income Journal Entry
Businesses record their financial transactions in the books of accounts on the basis o the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). A company following GAAP would record both interest revenue and interest receivables in the designated sections of the income statement. A company will either follow an accrual basis of accounting or a cash basis of accounting. This journal entry is made to eliminate the receivable that the company has recorded at the adjusting entry of the previous period. At the same time, it is to record the interest income that the company has earned during the current accounting period.
Financial Accounting
PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
Premium Investing Services
Interest revenue, also known as interest income, is the revenue earned by a company or individual from lending money or holding interest-bearing assets. It represents the compensation received for the use of money over a period of time and is a crucial component in the analysis of a company’s financial performance and profitability. Assume the 10% note from HWC to Cobalt in the amount of $200,000 is compounded annually, rather than daily or monthly, just to simplify this next calculation. Let’s also assume Cobalt follows GAAP, which means accrual-based accounting, and the company’s year-end for accounting purposes is December 31. This journal entry will eliminate the $150 of receivable that the company has recorded in the June 30 adjusting entry as well as recognize the 15 days of the interest income that the company has earned in July 2020. This journal entry is to recognize the $150 of interest income that the company has earned from its fixed deposit with XYZ Bank in the month of June 2020.
- A very simple example of interest income that happens every day is when an individual deposits money into a savings account and decides to leave it untouched for several months or years.
- Although IFRSs have fewer requirements on revenue recognition, the two main revenue recognition standards, IAS 18, Revenue and IAS 11, Construction Contracts, can be difficult to understand and apply.
- Interest revenue is the income earned from the lending of assets, whether it be money, goods or services.
- Interest Revenue can be defined as the earnings generated by a company from its lending or investing activities.
- This journal entry is made to eliminate the receivable that the company has recorded at the adjusting entry of the previous period.
Is interest revenue an expense?
As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. IFRS Accounting Standards are, in effect, a global accounting language—companies in more than 140 jurisdictions are required to use them when reporting on their financial health. The IASB is supported by technical staff and a range of advisory bodies. On the other hand, interest revenue may not be the primary source of income for different companies, such as automobile companies or electronics companies. In such cases, the interest income is generated for these companies from ancillary activities. These companies record interest income in the ‘Other Revenue and Expense’ section of the income statement.
CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path. In January, the clock starts ticking on the 16th, which means there is no interest accruing during the first 15 days, just the last 16. Interest accrues all through February, and the note is then due on the 75th day.
If an entity disposes of property, plant and equipment at the end of its useful economic life the proceeds of disposal are not revenue for the entity. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Interest Revenues account reports the interest earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement. Interest weighted average: what is it how is it calculated and used Revenues account includes interest earned whether or not the interest was received or billed. Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money. For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement.
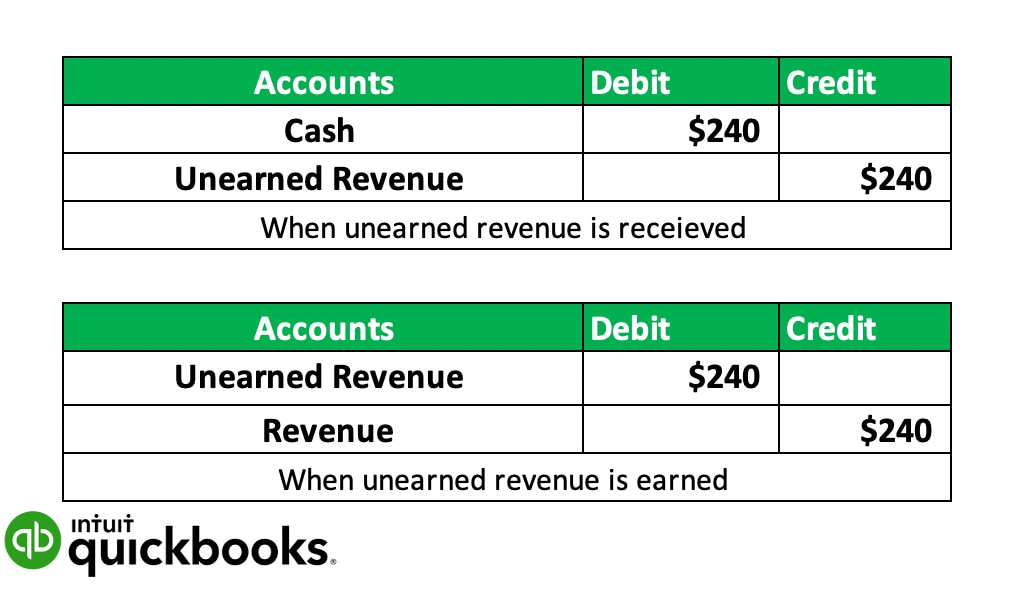
Most promissory notes have an explicit interest charge, and although some notes are labeled as “zero interest,” there is often a fee built into the note.
The backgroundAs already stated, revenue is a crucial number to users of financial statements in assessing an entity’s financial performance and position. However, revenue recognition requirements in US generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) differ from those in International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs).Both sets of requirements need improvement. US GAAP comprises broad revenue recognition concepts and numerous requirements for particular industries or transactions that can result in different accounting for economically similar transactions. Although IFRSs have fewer requirements on revenue recognition, the two main revenue recognition standards, IAS 18, Revenue and IAS 11, Construction Contracts, can be difficult to understand and apply. In addition, IAS 18 provides limited guidance on important topics such as revenue recognition for multiple-element arrangements.
